Nginx重要基础概念
connection
在core模块下有ngx_connection.h和Ngx_connection.c两个文件,从ngx_connection.h可以看到ngx_listening_s的数据结构:
struct ngx_connection_s {
/*
连接未使用时,data成员用于充当连接池中空闲连接链表中的next指针。当连接被使用时,data的意义由使用它的nginx模块而定,
如在HTTP框架中,data指向ngx_http_request_t请求
*/
void *data;
ngx_event_t *read; //连接对应的读事件
ngx_event_t *write; //连接对应的写事件
ngx_socket_t fd;
ngx_recv_pt recv;
ngx_send_pt send;
ngx_recv_chain_pt recv_chain;
ngx_send_chain_pt send_chain;
//这个连接对应的ngx_listening_t监听对象,此连接由listening监听端口的事件建立
ngx_listening_t *listening;
off_t sent;
ngx_log_t *log;
//内存池,一般在accept一个新连接时,会创建一个内存池,而在这个连接结束时会销毁内存池
ngx_pool_t *pool;
struct sockaddr *sockaddr;
socklen_t socklen;
ngx_str_t addr_text;
ngx_str_t proxy_protocol_addr;
#if (NGX_SSL)
ngx_ssl_connection_t *ssl;
#endif
struct sockaddr *local_sockaddr;
socklen_t local_socklen;
ngx_buf_t *buffer;
ngx_queue_t queue;
ngx_atomic_uint_t number;
ngx_uint_t requests;
unsigned buffered:8;
unsigned log_error:3; /* ngx_connection_log_error_e */
unsigned unexpected_eof:1;
unsigned timedout:1;
unsigned error:1;
unsigned destroyed:1;
unsigned idle:1;
unsigned reusable:1;
unsigned close:1;
unsigned sendfile:1;
unsigned sndlowat:1;
unsigned tcp_nodelay:2; /* ngx_connection_tcp_nodelay_e */
unsigned tcp_nopush:2; /* ngx_connection_tcp_nopush_e */
unsigned need_last_buf:1;
#if (NGX_HAVE_IOCP)
unsigned accept_context_updated:1;
#endif
#if (NGX_HAVE_AIO_SENDFILE)
unsigned busy_count:2;
#endif
#if (NGX_THREADS)
ngx_thread_task_t *sendfile_task;
#endif
};
struct ngx_listening_s {
ngx_socket_t fd; //socket套接字句柄
struct sockaddr *sockaddr; //监听socketaddr地址
socklen_t socklen; /* size of sockaddr */
size_t addr_text_max_len; //存储IP地址的字符串addr_text最大长度,即它指定了addr_text所分配的内存大小
ngx_str_t addr_text; //以字符串形式存储IP地址
int type; //套接字类型,当type是SOCK_STREAM时,表示TCP
int backlog;
int rcvbuf;
int sndbuf;
#if (NGX_HAVE_KEEPALIVE_TUNABLE)
int keepidle;
int keepintvl;
int keepcnt;
#endif
/* handler of accepted connection */
ngx_connection_handler_pt handler;
void *servers; /* array of ngx_http_in_addr_t, for example */
ngx_log_t log;
ngx_log_t *logp;
size_t pool_size;
/* should be here because of the AcceptEx() preread */
size_t post_accept_buffer_size;
/* should be here because of the deferred accept */
/* TCP_DEFER_ACCEPT 选项将在建立TCP连接成功且接收到用户的请求数据后,才向对监听套接字感兴趣的进程发送事件通知,而连接建立成功后,
如果post_accept_timeout 秒后仍然没有收到的用户数据,则内核直接丢弃连接
*/
ngx_msec_t post_accept_timeout;
ngx_listening_t *previous;
ngx_connection_t *connection;
unsigned open:1;
unsigned remain:1;
unsigned ignore:1;
unsigned bound:1; /* already bound */
unsigned inherited:1; /* inherited from previous process */
unsigned nonblocking_accept:1;
unsigned listen:1;
unsigned nonblocking:1;
unsigned shared:1; /* shared between threads or processes */
unsigned addr_ntop:1;
#if (NGX_HAVE_INET6 && defined IPV6_V6ONLY)
unsigned ipv6only:1;
#endif
unsigned keepalive:2;
#if (NGX_HAVE_DEFERRED_ACCEPT)
unsigned deferred_accept:1;
unsigned delete_deferred:1;
unsigned add_deferred:1;
#ifdef SO_ACCEPTFILTER
char *accept_filter;
#endif
#endif
#if (NGX_HAVE_SETFIB)
int setfib;
#endif
#if (NGX_HAVE_TCP_FASTOPEN)
int fastopen;
#endif
};
通过type=SOCK_STREAM,可以看出Nginx实际是对Tcp的封装,可以很方便地使用nginx封装好的connection来处理与连接相关的事情,包括建立、释放连接,发送、接收数据等。
建立连接的过程
- 解析配置文件,获取监听的端口和Ip地址。
- Nginx创建master进程,并建立socket(创建socket,设置addrreuse等选项,绑定到指定的ip地址端口,再listen),这样就可以创建多个worker进程来,每个worker进程都可以accept连接请求。
- 客户端与服务端通过三次握手成功建立一个连接后,nginx的某一个worker进程会accept成功,得到这个建立好的连接的socket,然后创建ngx_connection_t结构体,存储客户端相关内容,并设置读写事件处理函数并添加读写事件来与客户端进行数据的交换。
- 连接完成后客户端或者服务端主动关闭连接,释放掉ngx_connection_t结构体。
连接池
配置举例:
worker_processes 12;
events {
use epoll;
worker_connections 2048000;
}
在linux系统中,每一个进程能够打开的文件描述符fd是有限的。通过ulimit -n,可以得到一个进程所能够打开的fd的最大数,因为每个socket连接会占用掉一个fd,所以这也会限制我们进程的最大连接数,当然也会直接影响到我们程序所能支持的最大并发数,当fd用完后,再创建socket时,就会失败。Linux系统中open file resource limit的值可以通过如下方式修改:
echo "2390251" > /proc/sys/fs/file-max
sysctl -p
对于一个Nginx服务器来说,能创建的socket连接的最大数目可以达到worker_processes*worker_connections。
在反向代理环境中,最大并发数量应该是worker_connections*worker_processes/2。
nginx连接池实现原理见另一篇博客: 理解Nginx连接池
request
Nginx的request是指http请求,涉及到的数据结构为ngx_http_request_s,该数据结构贯穿了http请求的整个过程,可以说处理http请求就是操作ngx_http_request_t数据结构。
struct ngx_http_request_s {
uint32_t signature; /* "HTTP" */
ngx_connection_t *connection; //请求对应的客户端连接
void **ctx; //指向存放所有HTTP模块的上下文结构体的指针数组
void **main_conf; //指向请求对应的存放main级别配置结构体的指针数组
void **srv_conf; //指向请求对应的存放srv级别配置结构体的指针数组
void **loc_conf; //指向请求对应的存放loc级别配置结构体的指针数组
ngx_http_event_handler_pt read_event_handler;
ngx_http_event_handler_pt write_event_handler;
#if (NGX_HTTP_CACHE)
ngx_http_cache_t *cache;
#endif
ngx_http_upstream_t *upstream; //upstream机制用到的结构体,如果模块是load-balance的话设置这个
ngx_array_t *upstream_states;
/* of ngx_http_upstream_state_t */
ngx_pool_t *pool;
ngx_buf_t *header_in;
ngx_http_headers_in_t headers_in;
ngx_http_headers_out_t headers_out;
ngx_http_request_body_t *request_body;
time_t lingering_time; // 延迟关闭连接的时间
time_t start_sec;
ngx_msec_t start_msec;
ngx_uint_t method;
ngx_uint_t http_version;
ngx_str_t request_line;
ngx_str_t uri;
ngx_str_t args;
ngx_str_t exten;
ngx_str_t unparsed_uri;
ngx_str_t method_name;
ngx_str_t http_protocol;
ngx_chain_t *out;
/*
* 当前请求既可能是用户发来的请求,也可能是派生出的子请求,而main则标识一系列相关的派生子请求的原始请求
* 可以通过main和当前请求的地址是否相等来判断当前请求是否为用户发来的原始请求
*/
ngx_http_request_t *main;
ngx_http_request_t *parent;
ngx_http_postponed_request_t *postponed;
ngx_http_post_subrequest_t *post_subrequest;
ngx_http_posted_request_t *posted_requests;
ngx_int_t phase_handler;
ngx_http_handler_pt content_handler;
ngx_uint_t access_code;
ngx_http_variable_value_t *variables;
#if (NGX_PCRE)
ngx_uint_t ncaptures;
int *captures;
u_char *captures_data;
#endif
size_t limit_rate;
size_t limit_rate_after;
/* used to learn the Apache compatible response length without a header */
size_t header_size;
off_t request_length;
ngx_uint_t err_status;
ngx_http_connection_t *http_connection;
#if (NGX_HTTP_SPDY)
ngx_http_spdy_stream_t *spdy_stream;
#endif
ngx_http_log_handler_pt log_handler;
ngx_http_cleanup_t *cleanup;
unsigned subrequests:8;
unsigned count:8;
unsigned blocked:8;
unsigned aio:1;
unsigned http_state:4;
/* URI with "/." and on Win32 with "//" */
unsigned complex_uri:1;
/* URI with "%" */
unsigned quoted_uri:1;
/* URI with "+" */
unsigned plus_in_uri:1;
/* URI with " " */
unsigned space_in_uri:1;
unsigned invalid_header:1;
unsigned add_uri_to_alias:1;
unsigned valid_location:1;
unsigned valid_unparsed_uri:1;
unsigned uri_changed:1; //1表示URL发生过rewrite重写
unsigned uri_changes:4;
unsigned request_body_in_single_buf:1;
unsigned request_body_in_file_only:1;
unsigned request_body_in_persistent_file:1;
unsigned request_body_in_clean_file:1;
unsigned request_body_file_group_access:1;
unsigned request_body_file_log_level:3;
unsigned request_body_no_buffering:1;
unsigned subrequest_in_memory:1;
unsigned waited:1;
#if (NGX_HTTP_CACHE)
unsigned cached:1;
#endif
#if (NGX_HTTP_GZIP)
unsigned gzip_tested:1;
unsigned gzip_ok:1;
unsigned gzip_vary:1;
#endif
unsigned proxy:1;
unsigned bypass_cache:1;
unsigned no_cache:1;
/*
* instead of using the request context data in
* ngx_http_limit_conn_module and ngx_http_limit_req_module
* we use the single bits in the request structure
*/
unsigned limit_conn_set:1;
unsigned limit_req_set:1;
#if 0
unsigned cacheable:1;
#endif
unsigned pipeline:1;
unsigned chunked:1;
unsigned header_only:1;
unsigned keepalive:1;
unsigned lingering_close:1;
unsigned discard_body:1;
unsigned reading_body:1;
unsigned internal:1;
unsigned error_page:1;
unsigned filter_finalize:1;
unsigned post_action:1;
unsigned request_complete:1;
unsigned request_output:1;
unsigned header_sent:1; //1表示发送给客户端的HTTP响应头部已经发送
unsigned expect_tested:1;
unsigned root_tested:1;
unsigned done:1;
unsigned logged:1;
unsigned buffered:4;
unsigned main_filter_need_in_memory:1;
unsigned filter_need_in_memory:1;
unsigned filter_need_temporary:1;
unsigned allow_ranges:1;
unsigned single_range:1;
unsigned disable_not_modified:1;
#if (NGX_STAT_STUB)
unsigned stat_reading:1;
unsigned stat_writing:1;
#endif
/* used to parse HTTP headers */
ngx_uint_t state; //状态机解析HTTP时使用state表示当前的解析状态
ngx_uint_t header_hash;
ngx_uint_t lowcase_index;
u_char lowcase_header[NGX_HTTP_LC_HEADER_LEN];
u_char *header_name_start;
u_char *header_name_end;
u_char *header_start;
u_char *header_end;
/*
* a memory that can be reused after parsing a request line
* via ngx_http_ephemeral_t
*/
u_char *uri_start;
u_char *uri_end;
u_char *uri_ext;
u_char *args_start;
u_char *request_start;
u_char *request_end;
u_char *method_end;
u_char *schema_start;
u_char *schema_end;
u_char *host_start;
u_char *host_end;
u_char *port_start;
u_char *port_end;
unsigned http_minor:16;
unsigned http_major:16;
};
nginx处理http请求的具体过程:
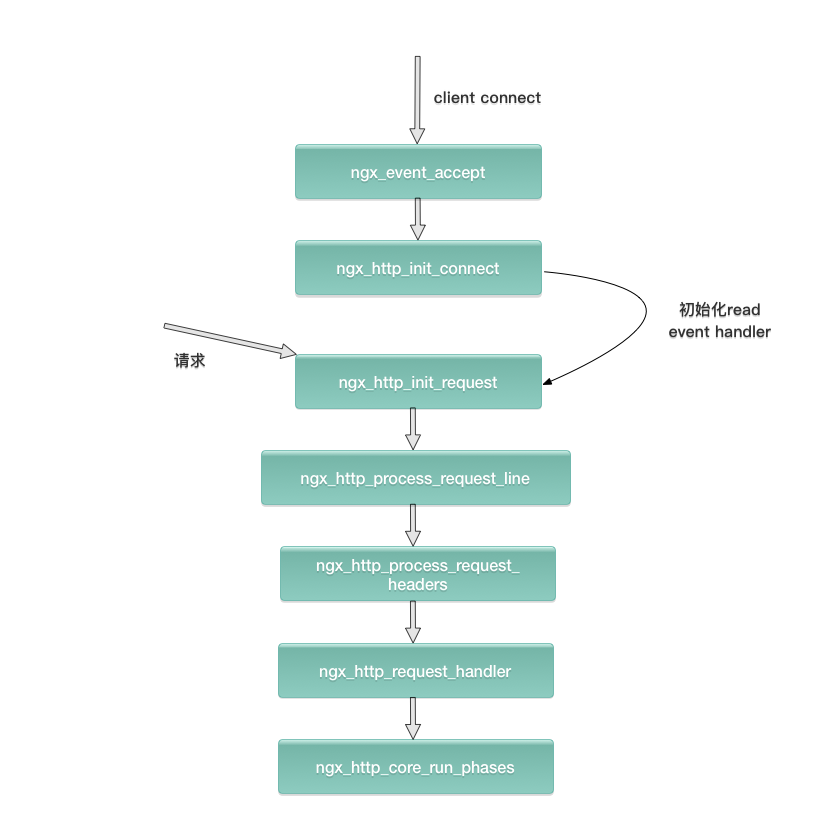
几个重要的相关概念:
-
keepalive
http请求是建立在TCP协议之上的,所以客户端在发起请求前需要与服务器经过三次握手建立tcp连接,同时关闭连接需要四次挥手。
http请求是请求应答式的,如果能知道每个请求头与响应体的长度,那么就可以在一个连接上面执行多个请求的,这就是长连接。如果客户端的请求头中的connection为close,则表示客户端需要关掉长连接,如果为keep-alive,则客户端需要打开长连接。如果客户端一直不发送数据过来,nginx不可能一直等待下去。为了避免一直占用此连接,nginx设置keepalive的同时也会设置最大等待时间keepalive_timeout,如果超过最大等待时间仍未收到任何数据,此时客户端的connection不管是close还是keepalive,都会强制close。
-
lingering_close
lingering_close的意思就是延迟关闭,当nginx要关闭连接时,并非立即关闭连接,而是先关闭tcp连接的写,再等待一段时间后再关掉连接的读。如果服务器直接强制关闭连接,此时刚好客户端发送消息,那么客户端就不会有收到ACK,导致出现没有任何错误信息的提示。
nginx官方网站建议lingering_close没有特殊原因都应打开,并且nginx默认值就是on。但打开后的副作用是系统的Response Time 大幅增加(空等数据)。tengine将lingering_close的默认值设为off。

